Stop Building Funnels: How to Engineer Growth Loops in AI Products
Most teams still design around funnels. I stopped doing that the moment I realized something fundamental: AI flips product physics. It turns linear user journeys into constantly adapting systems.
What I'm about to break down is the model I now use across AI products: four interlocking loops that compound without constant fuel.
And yes — I arrived at this idea myself while watching how Notion AI, Figma, Replit, and other AI-native tools behave in the wild.
What Is a Growth Loop, Really?

A growth loop is a closed system where the output of one cycle becomes the input of the next. In AI, this matters more than in classic SaaS because:
- every action produces data
- data improves models
- improved models increase user value
- increased value brings more users
- more users produce more data
This flywheel creates a compounding effect that no paid marketing campaign can match.
AI loops are not "nice-to-haves." They decide whether your model stays relevant or becomes fossilized within a quarter.
Core AI Growth Loop Types
Below are the most common and most powerful AI growth loops you can implement today.
1. Model-Improvement Loop (The Data Flywheel)
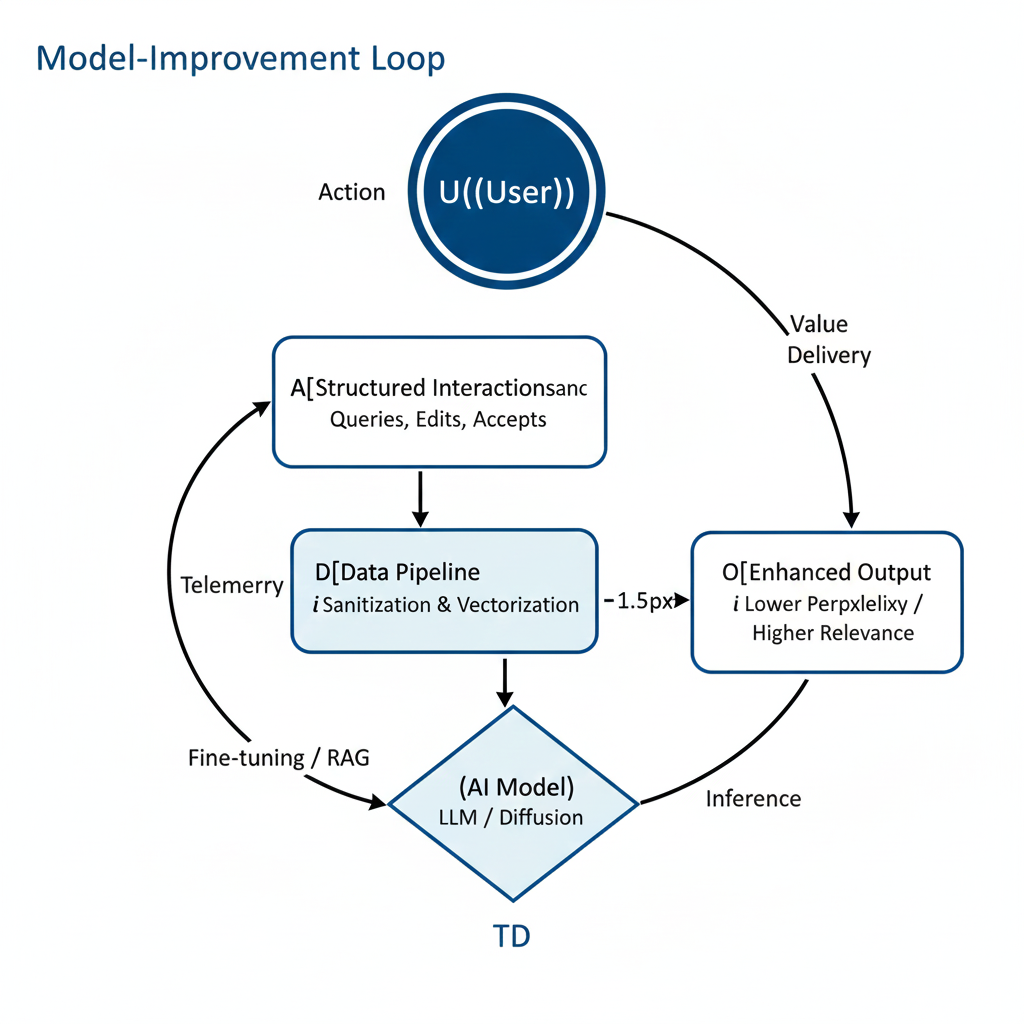
This is the fundamental loop behind almost every competitive AI product.
Mechanism: User activity generates fine-tuning data; this data improves the model; the improved model increases usage.
Loop Anatomy
- Input: A new user tries the model
- Action: They create structured interactions (queries, corrections, labeled outputs, usage patterns)
- Output: The system captures data
- Reinvestment: Data improves models, embeddings, ranking, retrieval, or workflows
- Cycle: Better predictions draw more users, creating more data
Example: ChatGPT/Replit AI / GitHub Copilot
The more developers use the AI, the more the model learns common coding mistakes and fixes. These improved suggestions attract more developers, which produce more training signals.
What makes this loop strong:
- Frictionless data capture
- Clear feedback channels
- Rapid model update cycles
- Value delivered immediately when the model improves
Weak data loops stagnate. Strong ones behave like accelerated evolution.
2. AI-UGC Loop (User-Generated Content, but Powered by AI)
UGC is already powerful. AI-UCG is stronger because it removes the expert barrier. Anyone can create something useful enough to attract new users.
Mechanism: AI helps users create valuable content; this content spreads; new users join; they create content too.
Input: User asks AI to generate, summarize, design, or produce content
Action: Output is published on a searchable or shareable surface
Output: Content attracts new users via SEO, embeds, or social platforms
Reinvestment: New users create more AI content, expanding the discovery surface
Example: Notion AI, Canva Magic Studio
Users generate documents, templates, and designs. These rank in Google Images, Pinterest, and workspaces. Each piece becomes an SEO node that pulls in more users.
Strength booster: A distribution-friendly output format (public pages, embeddable assets, shareable magic links)
3. Workflow Loop (The Automation Network)
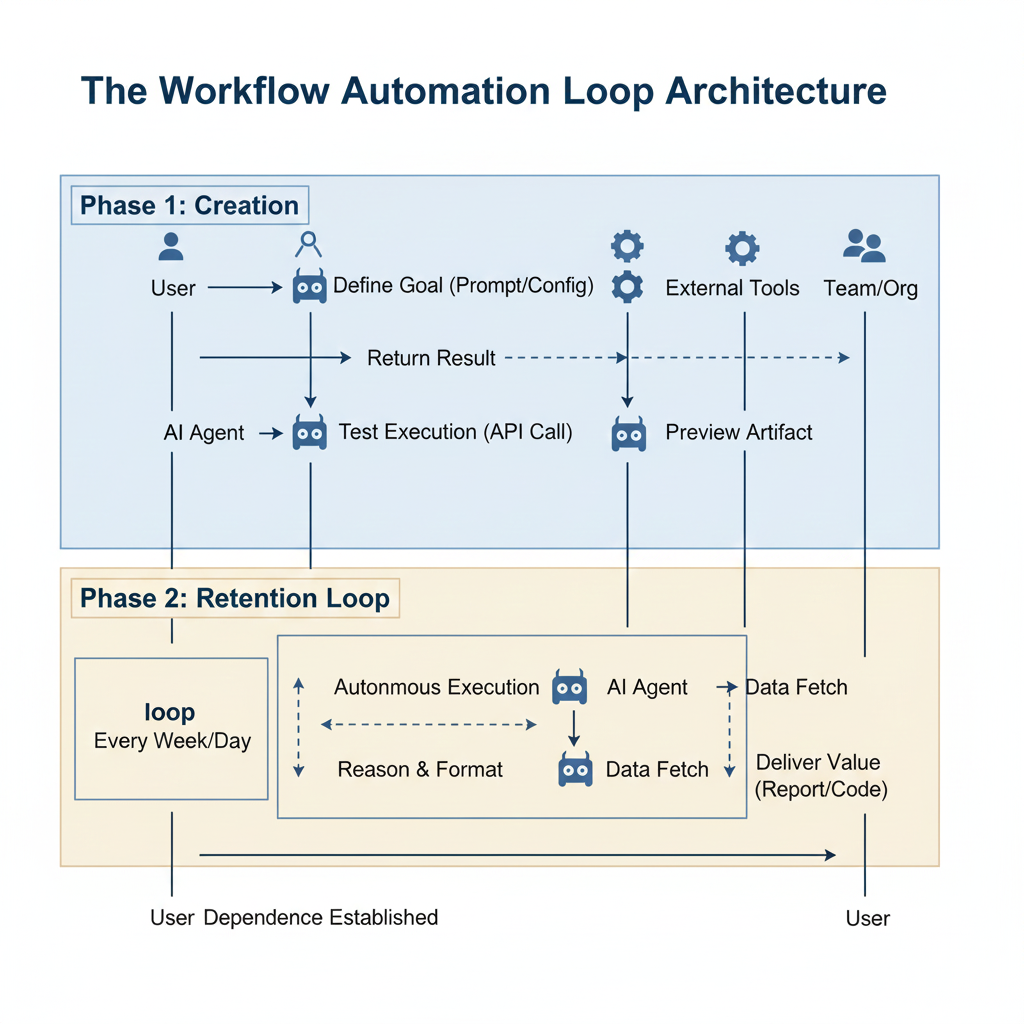
When users build automations or agents, each workflow becomes a long-lived retention magnet.
Mechanism: Users automate tasks; automations create recurring interactions; recurring interactions generate deeper lock-in.
Input: User sets up an AI workflow or agent
Action: Workflow executes repeatedly, producing results
Output: User becomes reliant
Reinvestment: Reliance spreads the workflow internally (team adoption), attracting more users
Example: Zapier AI or Airtable AI
One worker automates a reporting loop. The team sees the benefit. More workflows get created. Each workflow becomes a micro-channel for retention and referrals.
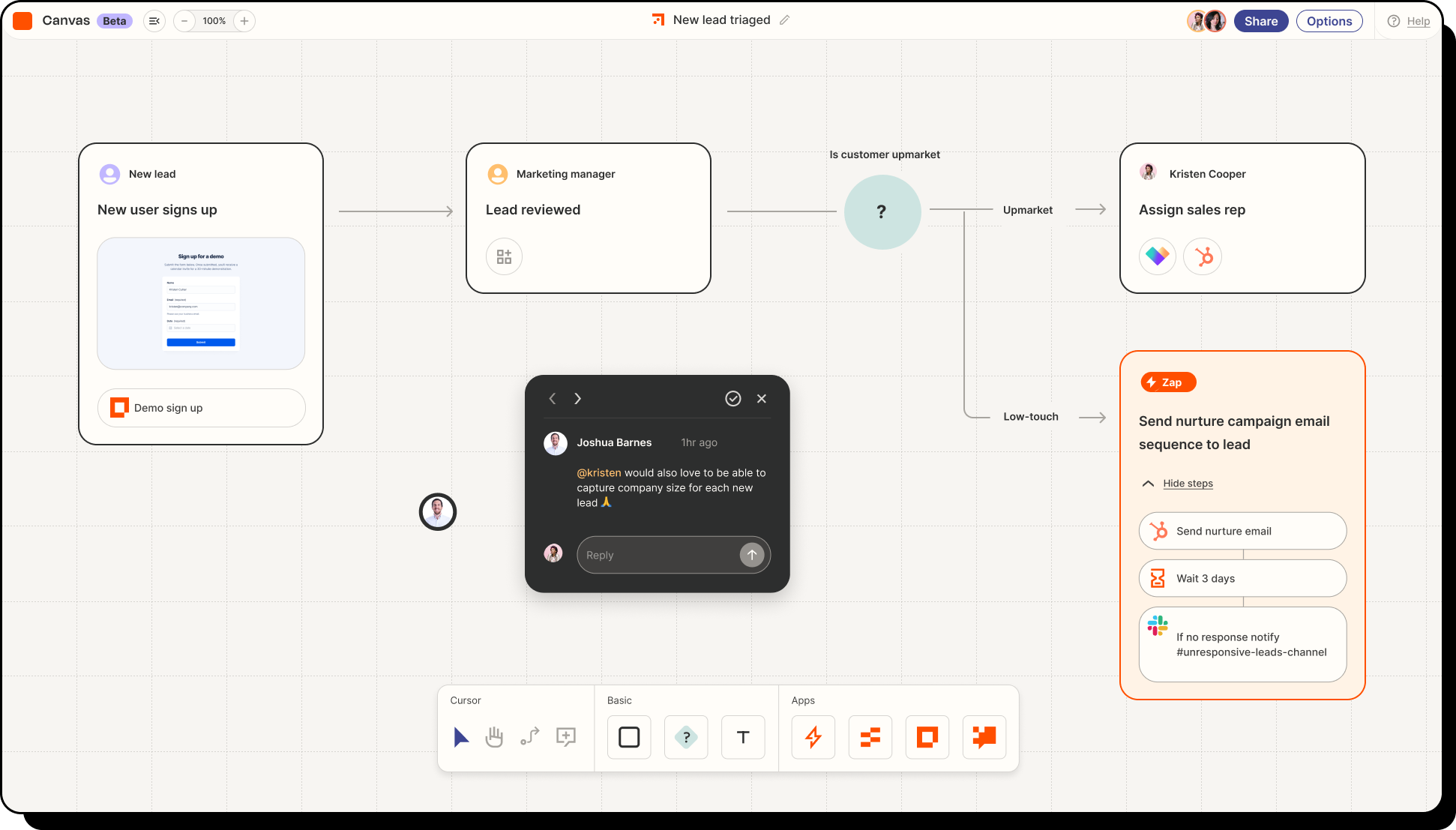
Source: https://zapier.com/blog/automate-new-zapier-products-free/
4. Collaboration Loop (Team-Based AI Expansion)
Teams adopt AI in clusters. One user almost always triggers the next three.
Mechanism: The product becomes more valuable when more teammates use it.
Input: Initial user starts a project or workspace
Action: They invite collaborators to unlock the full value
Output: New users join the workspace
Reinvestment: Group interactions multiply usage and visibility
Example: Figma AI, Slack AI
A single AI-powered file, board, or chat thread brings colleagues in. Collaboration becomes the viral vector.
5. Recommendation / Referral Loop (AI Makes Sharing Automatic)
AI creates high-quality artifacts. People share them because they are proud, curious, or seeking feedback.
Mechanism: AI outputs become referral objects.
Input: User generates something impressive
Action: They share it via link, template, or workflow export
Output: Their audience interacts
Reinvestment: Interaction drives new signups who then share too
Example: Runway or ElevenLabs
Videos, voices, assets: all naturally shareable. Every shared artifact is a viral node.
How to Choose the Right AI Growth Loop
Use this matrix:
| Loop Type | Best For | Key Ingredient |
|---|---|---|
| Model-Improvement | LLM tools, agents | High-quality structured data |
| AI-UCG / SEO | Content tools | Indexable outputs |
| Collaboration | Team productivity tools | Shared workspaces |
| Referral | Credits-based AI apps | Viral artifacts |
| Workflow | Automation/agent tools | Repeat usage |
| Trust (Review) | Recommendation or agent systems | Fast feedback cycles |
FAQ
Is this just a flywheel?
No. A flywheel accumulates momentum. An AI loop adapts — each cycle is smarter than the last.
Should we abandon funnels altogether?
Funnels still help structure acquisition. Loops describe what happens inside the product.
How do I measure loops?
I use:
- time to first meaningful output
- share rate of AI-generated content
- loop return frequency
- propagation events
- personalization depth score
Which categories benefit most?
Anything with repetitive cognition: writing, coding, design, learning, research, marketing.
Read More
If you enjoyed this post, you might also like: